NRC
Read the article in NRC
It is commonly known that research and development (R&D) of new medicines is very expensive, but there is much controversy with regard to how expensive it actually is. In thisstudy, we provide detailed and up-to-date insight into R&D costs of medicines using a novel,top-down model built on a single definition of pharmaceutical R&D costs and its principal drivers.
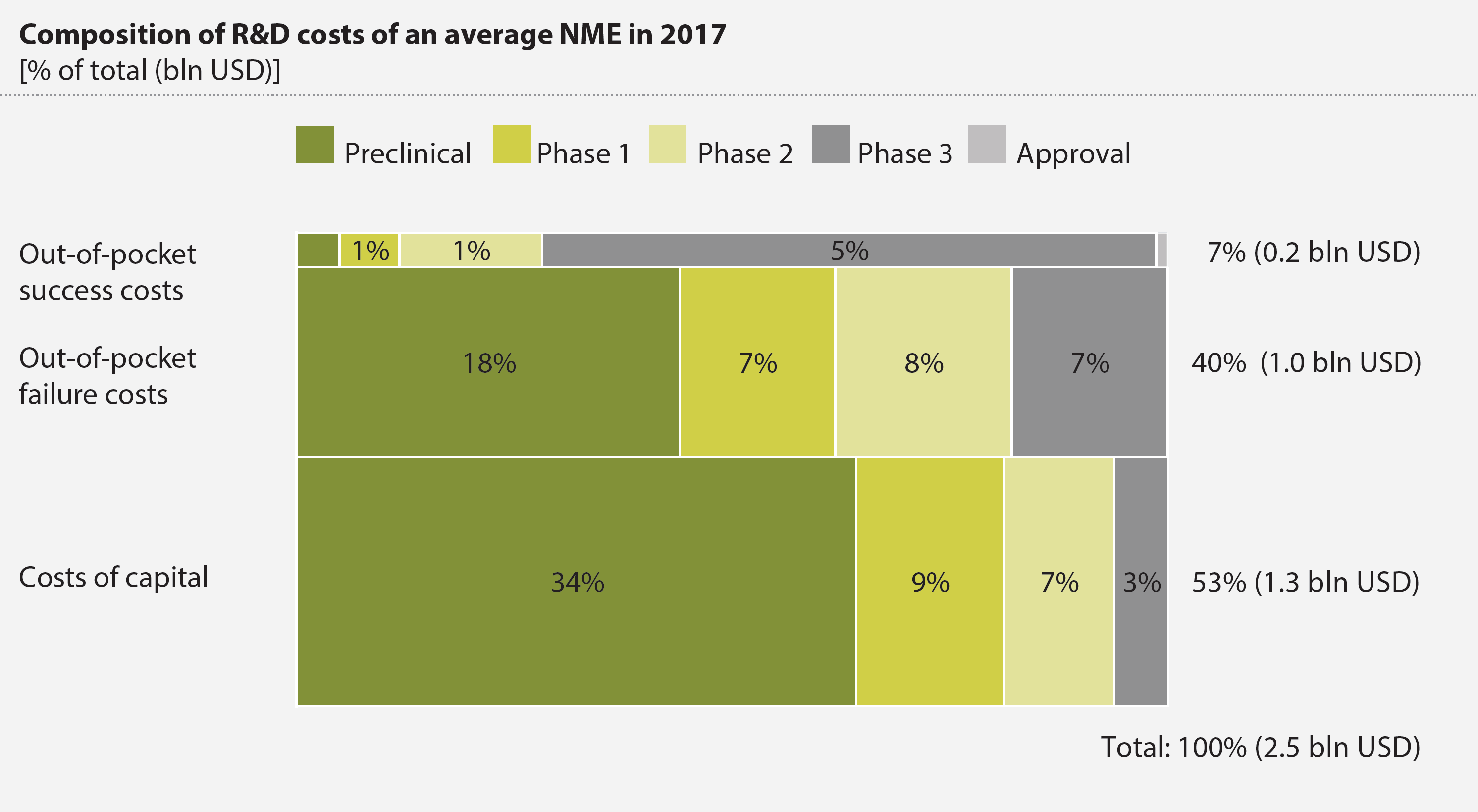
Our model shows that the average R&D costs per new molecular entity (NME) are 2.5 bln USD in 2017 (Figure 1). These costs are composed of out-of-pocket success costs (7%), out-of-pocket failure costs (40%) and costs of capital (53%). We also conclude that R&D costs differ substantially between different therapeutic areas: the average development costs of a medicine for an orphan disease could be as low as 0.5 bln USD, while the costs of a medicine
for an oncological disorder could be as high as 6.5 bln USD.
The insights of this study can help substantiate discussions on R&D costs with facts. Furthermore, they may help pharmaceutical companies, academic researchers and policymakers in their quest to increase the efficacy of R&D expenditure. While there is no lowhanging fruit, conceptually, this might be achieved in the following ways:
Download the full report 'The cost of oppurtunity' here »
Read the article in NRC
Read the article in Academie Nieuwezorg
Read the article in Skipr